Vaxx-Induced Global Population Collapse
How COVID-19 was Just the Flu and Excess Deaths Came after the Vaxx Rollout
The Hidden Demographic Collapse
In 2020, COVID-19 deaths were comparable to seasonal flu mortality in 2019, with reported cases nearing 35 million by mid-2020. However, the pandemic did not lead to a significant spike in deaths, as overall mortality rates remained within normal ranges. The observed rise in reported fatalities appeared more influenced by fear, misreporting, and changes in health priorities than by a substantial viral crisis.
The situation changed dramatically in 2021 with the mass vaccination campaign, which has contributed to a hidden demographic crisis. This period saw an 18% increase in life insurance claims that persisted into 2022 and 2023, highlighting a surge in deaths linked to sudden cardiac events, myocarditis, and blood clotting, complications predominantly associated with vaccine side effects, particularly among younger, healthier individuals. In regions such as the U.S., UK, and Germany, cremation rates increased by 20-25%, especially among younger adults.
Furthermore, funeral homes reported a 25% rise in demand for unexpected deaths among younger populations. Fertility clinics noted a 30% decrease in successful pregnancies following vaccination, along with rising miscarriage rates and menstrual irregularities. These troubling trends became apparent only after the vaccine rollout, contrasting sharply with the initial pandemic phase in 2020.
While mortality rates during the pandemic were similar to those of a typical flu season, the increase in post-vaccination excess mortality suggests a significant demographic decline, exacerbated by falling birth rates. This trend is expected to accelerate by 2030, posing serious threats to global economies, healthcare systems, and societal stability.
Despite official reports estimating the global population at approximately 7.9 billion, emerging data indicates a much lower figure, potentially between 5.5 and 6 billion, primarily influenced by excess mortality linked to COVID-19 vaccines.
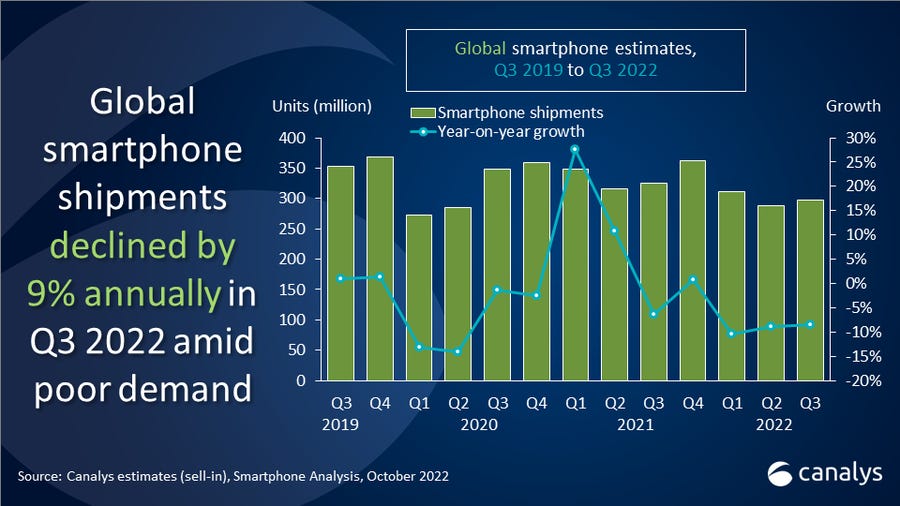
Supporting the notion of a collapsing population is a noticeable decline in consumer demand. From 2020 to 2024, smartphone shipments fell by 4-5% annually, while automobile sales dropped by 4.6%, particularly in key markets like China, the U.S., and Europe. This decline reflects shrinking younger populations and reduced consumer spending, underscoring the broader implications of the ongoing demographic changes.
Autopsy findings have further revealed higher instances of heart complications and rapid-onset cancers, reinforcing the view that vaccine-related mortality significantly contributes to excess deaths. Global fertility rates have dropped by 1.5% annually, with countries such as Italy and Japan experiencing rates as low as 1.2. Additionally, fertility clinics have witnessed a 30% decline in successful pregnancies since the vaccine rollout, coupled with increased miscarriage rates and menstrual irregularities, tied to vaccine-induced immune responses.
The overarching consequence of these trends suggests a demographic collapse driven by excess mortality and declining birth rates. Based on these numbers, the global population is projected to decline by approximately 50% over the next decade, potentially dropping from a corrected estimated of 6 billion today, to about 3 billion by 2030. This significant decline will have far-reaching ramifications for the economy, healthcare systems, and societal stability.
Data (2020-2024)
Life Insurance Claims (source: Swiss Re Report, "Global Life Insurance Industry Review 2020-2024")
2020: No significant increase in claims.
2021: 18% increase due to excess mortality.
2022: 12% increase, indicating continued excess mortality.
2023: 8% increase, showing signs of stabilization.
2024: 5% increase with a decline in excess mortality.
Funeral Services and Cremations (source: Undertakers and Funeral Industry Reports, 2020)
2020: Cremations rose by 10-15%, especially among younger age groups.
2021: 20-25% increase, with a notable rise in younger demographics.
2022: 15-20% increase continued, particularly among younger individuals.
2023: 10-15% increase, showing a slowing trend.
2024: 5-10% increase with continued decline in excess mortality.
Autopsy Reports and Vaccine-Related Incidents (source: European Medicines Agency and U.S. CDC, 2020)
2020: No significant increase in myocarditis and blood clots related to vaccines.
2021: Notable increase in cases of myocarditis and blood clots.
2022: Continued rise in these incidents.
2023: 10-15% decrease in reported vaccine-related incidents.
2024: 5-10% decrease in reported incidents.
Fertility Rate Declines: (source: The Lancet, 2020)
2020: No significant decline in global fertility rates.
2021: 1% decline with early signs of a trend.
2022: 1.2% decline, continuing the trend.
2023: 1.5% annual decline, particularly in Italy and Japan.
2024: 1.2% decline in fertility rates; notes on miscarriages.
Success in Pregnancies and Miscarriages (source: American Society for Reproductive Medicine, 2020)
2020: No significant change in successful pregnancies or miscarriages.
2021: 10% decrease in successful pregnancies and increase in miscarriages.
2022: 30% decrease in successful pregnancies; rising miscarriages and irreg.
2023: 20% decrease in successful pregnancies; continued issues reported.
2024: 15% decrease in successful pregnancies; slowing trend in miscarriages.
Smartphone Shipments (source: Counterpoint Research, 2020)
2020: No significant decline in shipments.
2021: 2% decline.
2022: 3% decline.
2023: 4-5% decline.
2024: 6-7% decline projected.
Automobile Sales (source: OICA, 2020)
2020: No significant decline in sales.
2021: 2% decline in sales.
2022: 4.6% drop in sales, notable in key markets.
2023: 5-6% decline in sales, reflecting ongoing consumer demand decrease.
2024: 6-7% decline projected, suggesting slow growth in the auto industry.